A. V. Dobromyslov, E. A. Kozlov, N. I. Taluts
DEFORMATION STRUCTURE OF HIGH-PURITY IRON AFTER EXPLOSIVE LOADING IN SPHERICAL SYSTEMS
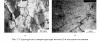
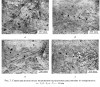
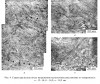
DOI: 10.17804/2410-9908.2016.6.069-079 The deformation structure of high-purity iron after loading by spherically converging shock waves is studied by optical metallography, transmission electron microscopy, and microhardness measurements. It is revealed that high-rate plastic deformation of iron proceeds by slip. Shear bands and bands of strain localization along grain boundaries are formed in the course of loading. A mixed structure consisting of dislocation cells and bands is observed at the microlevel. Under realized loading conditions, high-rate plastic deformation of iron proceeds in the ε-phase; therefore twins are not formed. The deformation structure of high-purity iron is compared with the structure of Armco iron formed after similar loading conditions. The found difference is explained by different mobility of dislocations.
Keywords: iron, shock waves, high-rate plastic deformation, structure References:
- Lan Y., Klaar H.I., Dahl W. Evolution of dislocation structure and deformation behavior of iron at different temperature: Part.I. Strain hardening curves and cellular structure. Metallurgical Transactions A, 1992, vol. 23, iss. 2, pp. 537–544. DOI: 10.1007/BF02801171.
- Arnold W. Dynamisches Werkstoffverhalten von ArmcoEisen bei Stoßwellenbelastung. Fortschr.-Ber. VDI Reihe 5 Nr. 247, Düsseldorf, Germany, VDI-Verlag, 1992, 248 S.
- Smith C.S., Fowler C.M. Further metallographic studies on metals after explosive shock. In: P.G. Shewmon and V.F. Zackay, eds. Response of Metals to High Velocity Deformation, Inter Science Publishers Inc., New York, 1961, pp. 309–341.
- Lobodyuk V.A., Savvakin G.I., Fedas N.P., Khandros L.G. Effect of shock waves on the change in the structure of Armco iron. In: Metallofizika: sbornik statey. Vyp. 53 [Metal Physics: Collection of Papers, iss. 53]. Kiev, Naukova Dumka Publ., 1974, pp. 46–50. (In Russian).
- Johnson J.N., Rohde R.W. Dynamic deformation twinning in shock-loaded iron. J. Appl. Phys., 1971, vol. 42, no. 11, pp. 4171–4182.
- Kozlov E.A., Telichko I.V., Gorbachev D.M., Pankratov D.G., Dobromyslov A.V., Taluts N.I. The metastability and incompleteness of the alpha-epsilon phase transformation in unalloyed iron loading pulses: Specific features under the effect of threshold of the deformation behavior and structure of armco iron. The Physics of Metals and Metallography, 2005, vol. 99, no. 3, pp. 300–313.
- Leslie W.C., Hornbogen E., Dieter G.E. The structure of shock-hardened iron before and after annealing. Journal of the Iron and Steel Institute, 1962, vol. 200, part 8, pp. 622–633.
- Altshuler L.V. The use of shock waves in high-pressure physics. Uspekhi fizicheskikh nauk, 1965, vol. 85, iss. 2, pp. 199–258. (In Russian).
- Zukas E.G., Fowler C.M. The behavior of iron and steel under impulsive loading. In: P.G. Shewmon and V.F. Zackay, eds. Response of Metals to High Velocity Deformation, Inter Science Publishers Inc., New York, 1961, pp. 343–369.
- Meyers M.F., Murr L.E. Defect generation in shock-wave deformation. In: M.F. Meyers, L.E. Murr, eds. Shock Waves and High-Strain-Rate Phenomena in Metals, Plenum Press, New York, 1981, pp.487–530.
- Dobromyslov A.V., Kozlov E.A., Taluts N.I. High-strain-rate deformation of armko iron induced by spherical and quasi-spherical converging shock waves and the mechanism of the α-ε transformation. The Physics of Metals and Metallography, 2008, vol. 106, no.5, pp. 531-541. DOI: 10.1134/S0031918X08110136.
- Kanel G.I., Razorenov S.V., Garkushin G.V., Ashitkov S.I., Komarov P.S., Agranat M.B. Deformation resistance and fracture of iron over a wide strain rate range. Physics of the Solid State, 2014, vol. 56, no. 8, pp. 1569–1573. DOI: 10.1134/S1063783414080113.
- Garkushin G.V., Naumova N.S., Atroshenko S.A., Razorenov S.V. Influence of the reversible α–ε phase transition and preliminary shock compression on the spall strength of armco iron. Technical Physics, 2016, vol. 61, no. 1, pp. 84–90. DOI: 10.1134/S1063784216010102.
- Kozlov E.A., Dobromyslov A.V., Taluts N.I., Voltz Ch. Effect of spherically converging shock waves on deformation and phase behavior of high-purity iron. The Physics of Metals and Metallography, 2012, vol. 113, no. 10, pp. 1007–1015. DOI: 10.1134/S0031918X12100055.
- Kamenetskaya D.S., Piletskaya I.B., Shiryaev V.I. Zhelezo vysokoy stepeni chistoty [High-Purity Iron]. Moscow, Metallurgiya Publ., 1978, 248 p. (In Russian).
- Maddin R., Chen N.K. Geometrical aspects of the plastic deformation of metals single crystals. In: B. Chalmers, R. King, eds. Progress in Metal Physics 5, Pergamon Press Ltd., London, 1954, vol. 5, pp. 69–125.
- Dobromyslov A.V., Dolgikh G.V., Taluts N.I, Shmatov V.T., Beresnev B.I. Influence of hydrostatic pressure upon geometry of slipping in monocrystals of siliceous iron. Fizika Metallov i Metallovedenie, 1982, vol. 54, iss. 2, pp. 332-338. (In Russian).
А. В. Добромыслов, Е. А. Козлов, Н. И. Талуц
ДЕФОРМАЦИОННАЯ СТРУКТУРА ВЫСОКОЧИСТОГО ЖЕЛЕЗА ПОСЛЕ ВЗРЫВНОГО НАГРУЖЕНИЯ В СФЕРИЧЕСКИХ СИСТЕМАХ
Методами металлографии, просвечивающей электронной микроскопии, а также измерением микротвердости изучена деформационная структура железа высокой чистоты после нагружения сферически сходящимися ударными волнами. Обнаружено, что высокоскоростная пластическая деформация железа осуществляется скольжением. В процессе нагружения происходит локализация деформации, приводящая к образованию полос сдвига, а в глубоких слоях шарового образца ‒ дополнительно полос локализации деформации по границам зерен. На микроуровне формируется смешанная структура, состоящая из ячеистой и полосовой структуры. При реализованных режимах нагружения высокоскоростная пластическая деформация протекает в ε-фазе, поэтому двойники не образуются. Проведено сравнение деформационной структуры высокочистого железа со структурой армко-железа, формирующейся после аналогичных условий нагружения.
Ключевые слова: железо, ударное нагружение, высокоскоростная пластическая деформация, структура Библиография:
- Lan Y., Klaar H. I., Dahl W. Evolution of dislocation structure and deformation behavior of iron at different temperature. Part. I. Strain hardening curves and cellular structure // Metallurgical Transactions A. ‒ 1992. ‒ Vol. 23, iss. 2. ‒ P. 537–544. ‒ DOI: 10.1007/BF02801171.
- Arnold W. Dynamisches Werkstoffverhalten von ArmcoEisen bei Stoßwellenbelastung. - Fortschr.-Ber. VDI Reihe 5 Nr. 247, Düsseldorf, Germany : VDI-Verlag, 1992. ‒ 248 S.
- Smith C. S., Fowler C. M. Further metallographic studies on metals after explosive shock // Response of Metals to High Velocity Deformation / edited by P. G. Shewmon, V. F. Zackay. - New York : Inter Science Publishers Inc., 1961. - P. 309-341.
- Воздействие ударных волн на изменение структуры армко-железа / В. А. Лободюк, Г. И. Саввакин, Н. П. Федас, Л. Г. Хандрос // Металлофизика : сб. науч. статей. ‒ Киев : Наукова думка, 1974. ‒ Вып. 53. ‒ С. 46‒50.
- Johnson J. N., Rohde R. W. Dynamic deformation twinning in shock-loaded iron // J. Appl. Phys. ‒ 1971. ‒ Vol. 42, no. 11. ‒ P. 4171‒4182.
- The metastability and incompleteness of the alpha-epsilon phase transformation in unalloyed iron loading pulses: Specific features under the effect of threshold of the deformation behavior and structure of armco iron / E. A. Kozlov, I. V. Telichko, D. M. Gorbachev, D. G. Pankratov, A. V. Dobromyslov, N. I. Taluts // The Physics of Metals and Metallography. ‒ 2005. ‒ Vol. 99, no. 3. – P. 300–313.
- Leslie W. C., Hornbogen E., Dieter G. E. The structure of shock-hardened iron before and after annealing // Journal of the Iron and Steel Institute. ‒ 1962. ‒ Vol. 200, part 8. ‒ P. 622‒633.
- Альтшулер Л. В. Применение ударных волн в физике высоких давлений // Успехи физических наук. - 1965. - Т. 85, вып. 2. - С. 199-258.
- Zukas E. G., Fowler C. M. The behavior of iron and steel under impulsive loading. // Response of metals to high velocity deformation / edited by P. G. Shewmon, V. F. Zackay. - New York : Inter Science Publishers Inc., 1961. - P. 343-369.
- Meyers M. F., Murr L. E. Defect generation in shock-wave deformation // Shock waves and high-strain-rate phenomena in metals /edited by M. A. Meyers, L. E. Murr. ‒ New York : Plenum Press, 1981. ‒ Р. 487–530.
- Dobromyslov A. V., Kozlov E. A., Taluts N. I. High-strain-rate deformation of armko iron induced by spherical and quasi-spherical converging shock waves and the mechanism of the α-ε transformation // The Physics of Metals and Metallography. ‒ 2008. ‒ Vol. 106, no. 5. ‒ P. 531-541. ‒ DOI: 10.1134/S0031918X08110136.
- Deformation resistance and fracture of iron over a wide strain rate range / G. I. Kanel, S. V. Razorenov, G. V. Garkushin, S. I. Ashitkov, P. S. Komarov, M. B. Agranat // Physics of the Solid State. – 2014. – Vol. 56, no. 8. – P. 1569–1573. – DOI: 10.1134/S1063783414080113.
- Influence of the reversible α–ε phase transition and preliminary shock compression on the spall strength of armco iron / G. V. Garkushin, N. S. Naumova, S. A. Atroshenko, S. V. Razorenov // Technical Physics. – 2016. – Vol. 61, no. 1. – P. 84–90. – DOI: 10.1134/S1063784216010102.
- Effect of spherically converging shock waves on deformation and phase behavior of high-purity iron / E. A. Kozlov, A. V. Dobromyslov, N. I. Taluts, Ch. Voltz // The Physics of Metals and Metallography. – 2012. – Vol. 113, no. 10. – P. 1007–1015. – DOI: 10.1134/S0031918X12100055.
- Каменецкая Д. С., Пилецкая И. В., Ширяев В. И. Железо высокой степени чистоты. ‒ M. : Металлургия, 1978. ‒ 248 с.
- Maddin R., Chen N. K. Geometrical aspects of the plastic deformation of metals single crystals // Progress in Metal Physics 5 / edited by B. Chalmers, R. King. ‒ London : Pergamon Press Ltd., 1954. ‒ Vol. 5. ‒ P. 69‒125.
- Influence of hydrostatic pressure upon geometry of slipping in monocrystals of siliceous iron / A. V. Dobromyslov, G. V. Dolgikh, N. I. Taluts, V. T. Shmatov, B. I. Beresnev // Fizika metallov i metallovedenie. ‒ 1982. ‒ Vol. 54, iss. 2. ‒ P. 332-338.
Библиографическая ссылка на статью
Dobromyslov A. V., Kozlov E. A., Taluts N. I. Deformation Structure of High-Purity Iron after Explosive Loading in Spherical Systems // Diagnostics, Resource and Mechanics of materials and structures. -
2016. - Iss. 6. - P. 69-79. - DOI: 10.17804/2410-9908.2016.6.069-079. -
URL: http://dream-journal.org/issues/2016-6/2016-6_110.html (accessed: 03.11.2025).
|