A. V. Dobromyslov, N. I. Taluts
AN ELECTRON-MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF THE DEFORMATION STRUCTURE OF THE 12Kh18N10T STEEL AFTER EXPLOSIVE LOADING IN SPHERICAL SYSTEMS
DOI: 10.17804/2410-9908.2015.5.109-117 Optical metallography, transmission electron microscopy and microhardness measurements are used to investigate the deformed structure of retained shells made of the 12Kh18N10T steel after explosive loading. It has been established that the high-rate plastic deformation of the steel under this loading occurs both by slipping and twinning. It is shown that there is a strong localization of deformation resulted in the formation of rough traces of slip. The high pressure at the shock wave front results in the fact that the critical shear stress in one grain is achieved in several slip systems simultaneously, irrespective of the Schmid factor. Therefore, several nonequivalent systems become active slip systems at once. Microtwins form large clusters in which they mainly belong to one or two systems of twinning. The average thickness of microtwins is ~ 30‒40 nm. Polymorphic γ → α transformation has been revealed under explosive loading. The α-phase is observed in the form of fine precipitates. It has been found that the microhardness almost doubles after shock loading, as compared with that of the initial state.
Keywords: 12Kh18N10T steel, shock waves, high-rate plastic deformation, structure References:
- Meyers M.F., Murr L.E. Defect generation in shock-wave deformation. In: M.A. Meyers, L.E. Murr, eds. Shock waves and high-strain-rate phenomena in metals. New York, Plenum Press, 1981, pp. 487–530.
- Sencer B.H., Maloy S.A., Gray III G.T. The influence of explosive-driven shock prestraining at 35 GPa and of high deformation on the structure/property behavior of 316 L austenitic stainless steel. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A: Physical Metallurgy and Materials Science, 2005, vol. 36, iss. 7, pp. 1825–1831. DOI: 10.1016/j.actamat.2005.03.037.
- Lee Woel-Shyan, Lin Chi-Feng. Comparative study of the impact response and microstructure of 304L stainless steel with and without prestrain. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2002, vol. 33, issue 9, pp. 2801–2810. DOI: 10.1007/s11661-002-0265-4.
- Murr L.E., Staudhammer K.P., Hecker S.S. Effects of Strain State and Strain Rate on Deformation-Induced Transformation in 304 Stainless Steel: Part II. Microstructural Study. Metallurgical Transactions A, 1982, vol. 13, iss. 4, pp. 627–635. DOI: 10.1007/BF02644428.
- Malloy S.A., Gray III G. T., Cady C.M., Rutherford R.W., Hihson R.S. The influence of explosive-driven “taylor-wave” shock prestraining on the structure/property behavior of 304 stainless steel. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2004, vol. 35, iss. 9, pp. 2617–2624. DOI: 10.1007/s11661-004-0207-4.
- Firraro D., Matteis P., Scavino G., Ubertalli G., Ienco M. G., Pellati G., Piccardo P., Pinasco M.R., Stagno E., Montanari R., Tata M.E., Brandimarte G., Petralia S., Mechanical twins in 304 stainless steel after small-charge explosion. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2006, vol. 424, iss. 1–2, pp. 23–32. DOI: 10.1016/j.msea.2006.02.036.
- Kozlov E.A., Brichikov S.A., Boyarnikov D.S., Kuchko D.P., Degtyarev A.A. Special features in convergence dynamics of steel shells under their explosive loading. Results of laser-interferometric measurements. The Physics of Metals and Metallography, 2011, vol. 112, iss. 4, pp. 389–404. DOI: 10.1134/S0031918X11040259.
- Rutkowska-Gorczyca M., Podrez-Radziszwska M., Kajtoch J. Corrosion resistance and microstructure of steel AISI 316L after cold plastic deformation. Metallurgy and foundry engineering, 2009, vol. 35, no. 1, pp. 35–42.
- Borodin E.N., Atroshenko S. A., Mayer A.E. Distribution of dislocations and twins in copper and 18Cr-10Ni-Ti steel under shock-wave loading. Technical Physics, 2014, vol. 59, iss. 8, pp. 1163–1170. DOI: 10.1134/S1063784214080076.
- Bogers A.J., Burgers W.G. Partial dislocations on the {110} planes in the B.C.C. lattice and the transition of the F.C.C. into the bcc lattice. Acta Metallurgica, 1964, vol. 12, iss. 2, pp. 255–261. DOI: 10.1016/0001-6160(64)90194-4.
- Talonen J., Hanninen H. Formation of shear bands and strain-induced martensite during plastic deformation of metastable austenitic stainless steels. Acta Materialia, 2007, vol. 55, iss. 18, pp. 6108–6118. DOI: 10.1016/j.actamat.2007.07.015.
- Zel'dovich V.I., Kheifets A.E., Frolova N.Yu., Muzyrya A.K., Simonov A.Yu. Formation of martensite in austenitic steel upon loading by quasi-spherical converging shock waves. The Physics of Metals and Metallography, 2013, vol. 114, iss. 12, pp. 1031–1037. DOI: 10.1134/S0031918X13120090.
А. В. Добромыслов, Н. И. Талуц
ЭЛЕКТРОННО-МИКРОСКОПИЧЕСКОЕ ИССЛЕДОВАНИЕ ДЕФОРМАЦИОННОЙ СТРУКТУРЫ СТАЛИ 12Х18Н10Т ПОСЛЕ ВЗРЫВНОГО НАГРУЖЕНИЯ В СФЕРИЧЕСКИХ СИСТЕМАХ
Изучена деформационная структура сохраненных оболочек из нержавеющей аустенитной стали 12Х18Н10Т после взрывного нагружения. Установлено, что высокоскоростная пластическая деформация стали в условиях ударного нагружения осуществляется как скольжением, так и двойникованием. Показано, что в процессе деформации происходит сильная локализация деформации, приводящая к образованию грубых следов скольжения. Высокое давление на фронте ударной волны приводит к тому, что критическое напряжение сдвига в одном зерне достигается сразу же в нескольких системах, независимо от фактора Шмида, в результате чего активными системами скольжения становятся несколько неэквивалентных систем. Обнаружено, что микродвойники формируют большие скопления, в которых они в основном принадлежат к одной или двум системам двойникования. Средняя толщина микродвойников составляет ~ 30‒40 нм. Обнаружено, что при взрывном нагружении протекает полиморфное γ → α превращение. Образующаяся α-фаза наблюдается в виде мелких выделений. Установлено, что значение микротвердости после ударного нагружения увеличилось примерно в 2 раза по сравнению с исходным состоянием.
Ключевые слова: сталь 12Х18Н10Т, ударное нагружение, высокоскоростная пластическая деформация, структура Библиография:
- Meyers M. F., Murr L. E. Defect generation in shock-wave deformation // Shock waves and high-strain-rate phenomena in metals / M. A. Meyers, L. E. Murr, eds. – New York: Plenum Press. 1981. P. 487–530.
- Sencer B. H., Maloy S. A., Gray III G. T. The influence of explosive-driven shock prestraining at 35 GPa and of high deformation on the structure/property behavior of 316 L austenitic stainless steel // Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A: Physical Metallurgy and Materials Science. 2005. – Vol. 36, iss. 7. – P. 1825–1831. – DOI: 10.1016/j.actamat.2005.03.037.
- Lee Woel-Shyan, Lin Chi-Feng. Comparative study of the impact response and microstructure of 304L stainless steel with and without prestrain // Metallurgical and Materials Transactions – 2002. – Vol. 33, iss. 9. – P. 2801–2810. – DOI: 10.1007/s11661-002-0265-4.
- Murr L. E., Staudhammer K. P., Hecker S. S. Effects of Strain State and Strain Rate on Deformation-Induced Transformation in 304 Stainless Steel: Part II. Microstructural Study // Metallur[1]gical Transactions A. – 1982. – Vol. 13, iss. 4. – P. 627–635. – DOI: 10.1007/BF02644428.
- The influence of explosive-driven “taylor-wave” shock prestraining on the structure/property behavior of 304 stainless steel / S. A. Malloy, G. T. Gray III, C. M. Cady, R. W. Rutherford, R. S. Hihson // Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A. – 2004. – Vol. 35, iss. 9. – P. 2617–2624. – DOI: 10.1007/s11661-004-0207-4.
- Mechanical twins in 304 stainless steel after small-charge explosion / D. Firraro, P. Matteis, G. Scavino, G. Ubertalli, M. G. Ienco, G. Pellati, P. Piccardo, M. R. Pinasco, E. Stagno, R. Montanari, M. E. Tata, G. Brandimarte, S. Petralia // Materials Science and Engineering: A. – 2006. – Vol. 424, iss 1–2, P. 23–32. DOI: 10.1016/j.msea.2006.02.036.
- Special features in convergence dynamics of steel shells under their explosive loading. Results of laser-interferometric measurements / E. A. Kozlov, S. A. Brichikov, D. S. Boyarnikov, D. P. Kuchko, A. A. Degtyarev // The Physics of Metals and Metallography. – 2011. – Vol. 112, iss. 4. – P. 389–404. – DOI: 10.1134/S0031918X11040259.
- Rutkowska-Gorczyca M., Podrez-Radziszwska M., Kajtoch J. Corrosion resistance and microstructure of steel AISI 316L after cold plastic deformation // Metallurgy and foundry engineering. – 2009. – Vol. 35, no. 1. – P. 35–42.
- Borodin E. N., Atroshenko S. A., Mayer A. E. Distribution of dislocations and twins in copper and 18Cr-10Ni-Ti steel under shock-wave loading // Technical Physics. – 2014. – Vol. 59, iss. 8. – P. 1163–1170. – DOI: 10.1134/S1063784214080076.
- Bogers A. J., Burgers W. G. Partial dislocations on the {110} planes in the B.C.C. lattice and the transition of the F.C.C. into the bcc lattice // Acta Metallurgica. – 1964. – Vol. 12, iss. 2. – P. 255–261. – DOI: 10.1016/0001-6160(64)90194-4.
- Talonen J., Hanninen H. Formation of shear bands and strain-induced martensite during plastic deformation of metastable austenitic stainless steels // Acta Materialia. – 2007. – Vol. 55, iss. 18. – P. 6108–6118. – DOI: 10.1016/j.actamat.2007.07.015.
- Formation of martensite in austenitic steel upon loading by quasi-spherical converging shock waves / V. I. Zel'dovich, A. E. Kheifets, N. Yu. Frolova, A. K. Muzyrya, A. Yu. Simonov // The Physics of Metals and Metallography. – 2013. – Vol. 114, iss. 12. – P. 1031–1037. – DOI: 10.1134/S0031918X13120090.
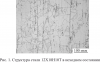 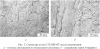 ![Рис. 3. Тонкие микродвойники в стали 12Х18Н10Т после нагружения: а – светлополь- ное изображение; б – микроэлектронограмма к (а), ось зоны основной ориентации [110]; в – темнопольное изображение, полученное в матричном рефлексе (1 1 1 ) γ; г – темнопольно](/netcat_files/multifile/2664/preview_3_21.png) 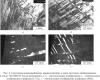 ![Рис. 5. Выделения α-фазы, образовавшиеся в стали 12Х18Н10Т после ударного нагружения: а – светлопольное изображение; б – микроэлектронограмма к (а), ось зоны [112]γ; в – темнопольное изображение, полученное в рефлексе (002)γ; г – микроэлектронограмма к ри](/netcat_files/multifile/2664/preview_5_14.png) 
Библиографическая ссылка на статью
Dobromyslov A. V., Taluts N. I. An Electron-Microscopic Study of the Deformation Structure of the 12kh18n10t Steel after Explosive Loading in Spherical Systems // Diagnostics, Resource and Mechanics of materials and structures. -
2015. - Iss. 5. - P. 109-117. - DOI: 10.17804/2410-9908.2015.5.109-117. -
URL: http://dream-journal.org/issues/2015-5/2015-5_51.html (accessed: 26.03.2025).
|